What is Metal Injection Molding (MIM)?
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) is an advanced manufacturing process that combines the design flexibility of plastic injection molding with the strength and integrity of sintered metal. Ideal for producing small, complex, and high-volume metal parts, MIM outperforms traditional methods like machining, casting, or stamping in cost-effectiveness and precision. As a leading China Precision Metal Injection Mould Factory, we specialize in delivering high-quality MIM solutions for diverse industries.
MIM products boast a wide range of applications and promising market prospects. For example:
Computers & Peripheral Equipment: Printer components, magnetic cores, striker pins, drive parts.
Tools: Gun drills, drill chucks, components for power tools and hand tools, wrench parts, milling cutter heads, nozzles.
Household Appliances & Goods: Watch cases, watch bands, electric toothbrushes, scissors, fans, golf club heads, imitation jewelry, knife heads, e-cigarette components.
Medical Device Components: Orthodontic brackets, surgical scissors, tweezers.
Military & Ordnance Components: Missile fins, firearm parts, projectile heads, liners, fuse components.
Electrical Components: Micro-motor parts, electronic components, sensor elements, mobile phone and pager parts.
Mechanical Components: Various small, complex parts for machines like cotton loosening machines, textile machinery, sewing machines, and office equipment.
Automotive & Marine Components: Clutch inner rings, rocker arm inserts, shift fork bushings, distributor sleeves, automotive airbag parts, automotive locks.
Oilfield Drilling Tools: Various specialized hard alloy nozzles, etc.
Advantages of MIM
Fundamentally, MIM is a process highly suitable for the mass production of components characterized by high-melting-point materials, high strength, and complex geometries. Its advantages can be summarized as follows:
a. Capable of producing complex-shaped metal parts in a single molding process, similar to plastic injection molding.
b. Low product cost, excellent surface finish, and high precision (±0.3% ~ ±0.1%), typically eliminating the need for secondary machining.
c. Superior mechanical properties such as product strength, hardness, and elongation; excellent wear resistance, good fatigue resistance, and a uniform microstructure.
d. High material utilization rate, a high degree of production automation, simplified process flow, enabling continuous, high-volume production.
e. Facilitates the use of multi-cavity molds for high forming efficiency, long mold service life, and quick and easy mold changes and adjustments.
f. The feedstock can be reused, achieving a material utilization rate of over 98%.
g. Particularly suited for mass production, ensuring excellent product consistency. The economic benefits increase with higher production volumes for appropriately selected parts.
h. Wide range of applicable materials, including carbon steel, alloy steel, tool steel, refractory alloys, cemented carbides, and high-density alloys. Applications are vast, spanning virtually all sectors of the national economy.
i. An environmentally friendly, clean production process.
The choice of metal forming process is primarily determined by two factors: part complexity and production volume. The MIM process holds a distinct advantage for parts with high complexity and large production quantities. For part designers, the focus should be on designing highly complex, three-dimensional parts for mass production to fully leverage the characteristics of the MIM process, thereby achieving reduced production costs and enhanced product performance.
Common MIM Materials and Their Application Fields
| Material Category | Material Designation | Application Fields |
| Iron Alloys | Fe-2Ni, Fe-8Ni | Structural components for automotive and machinery industries |
| Stainless Stee | 316L, 17-4PH, 420, 440C | Medical devices, watch components |
| Cemented Carbide | WC-Co | Cutting tools, timepiece parts |
| Ceramics | Al₂O₃, ZrO₂, SiO₂ | IT electronics, daily necessities, watches |
| Heavy Alloys | W-Ni-Fe, W-Ni-Cu, W-Cu | Communication equipment, consumer goods |
| Titanium Alloys | Ti, Ti-6Al-4V | Medical, aerospace |
| Magnetic Materials | Fe, Fe-50Ni, Fe-Si | Various magnetic components |
| Tool Steel | 42CrMo4, M2 | Various tools |
Advantages of MIM Mold Processing
High Geometric Design Freedom: Enables the production of complex-shaped metal components in a single molding process, similar to plastic injection molding.
Uniform Density and Excellent Surface Finish: Achieves a surface roughness of Ra 0.80–1.6 μm, suitable for parts weighing between 0.1–200 grams, with high dimensional accuracy (0.1%–0.3%), typically eliminating the need for secondary machining.
Wide Range of Material Compatibility: Applicable to various metal materials, including stainless steels, alloys, and cemented carbides.
High Production Efficiency and Cost Reduction: Features high material utilization, a high degree of automation, and streamlined processes, enabling continuous, high-volume production.
Stable Quality and Reliable Performance: Produces parts with a relative density of 95%–99%. Components can undergo heat treatments such as carburizing, quenching, and tempering, resulting in excellent mechanical properties including strength, hardness, and elongation, alongside good wear resistance, fatigue resistance, and a uniform microstructure.
Design and Manufacturing of MIM Molds
The MIM mold is a critical tool in the Metal Injection Molding process, whose design and manufacturing significantly influence part quality, molding efficiency, and production costs. MIM molds typically contain internal cavities into which a feedstock of metal powder and polymer binder is injected to form the desired component shape. During the injection molding process, the mold controls pressure, temperature, and material flow, ensuring the feedstock completely fills the cavity and forms the intended geometry. Manufacturing MIM molds requires high-precision machining capabilities, utilizing technologies such as CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), and wire cutting.
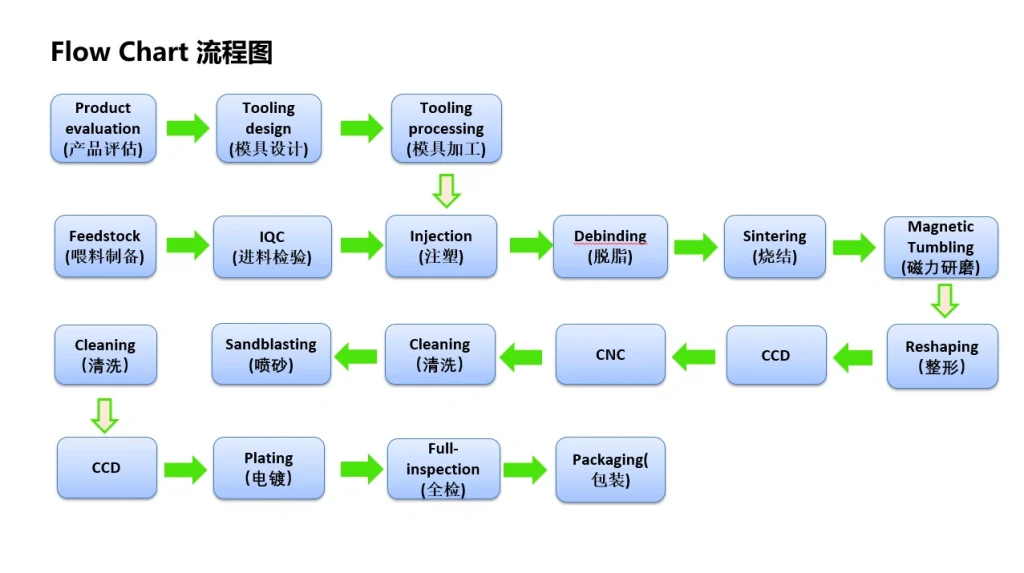
Metal injection molding flow chart